Platinum is the principal metal of the six-metal group that bears its name; the other platinum group metals are palladium, rhodium, ruthenium, osmium, and iridium. All possess unique chemical and physical qualities that make them vital industrial materials.
Jewelry creates the largest demand for platinum, accounting for 51%. Automotive catalysts take 29% and chemical and petroleum refining catalysts, 13%.
Platinum is used in the computer industry and in other high-tech electronic applications since it is an excellent conductor of electricity, does not corrode, and has a low reactivity with other metals. This sector accounts for about 7% of consumption.
Platinum is among the world's scarcest metals; new mine production totals approximately only 5 million troy ounces a year. In contrast, gold mine production runs approximately 82 million ounces a year, and silver production is approximately 547 million ounces.
Supplies of platinum are concentrated in South Africa, which accounts for approximately 80% of supply; Russia, 11%; and North America, 6%.
Because of the metal's importance as an industrial material, its relatively low production, and concentration among a few suppliers, prices can be volatile. For this reason, it is often considered attractive to investors.
Trading Unit 50 troy ounces.
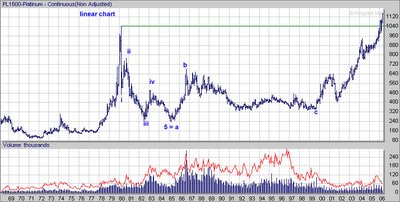
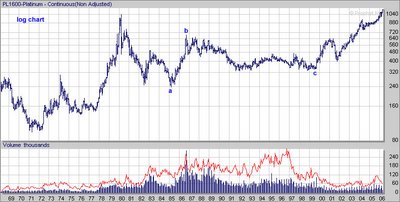
Gold & Silver spot charts




No comments:
Post a Comment